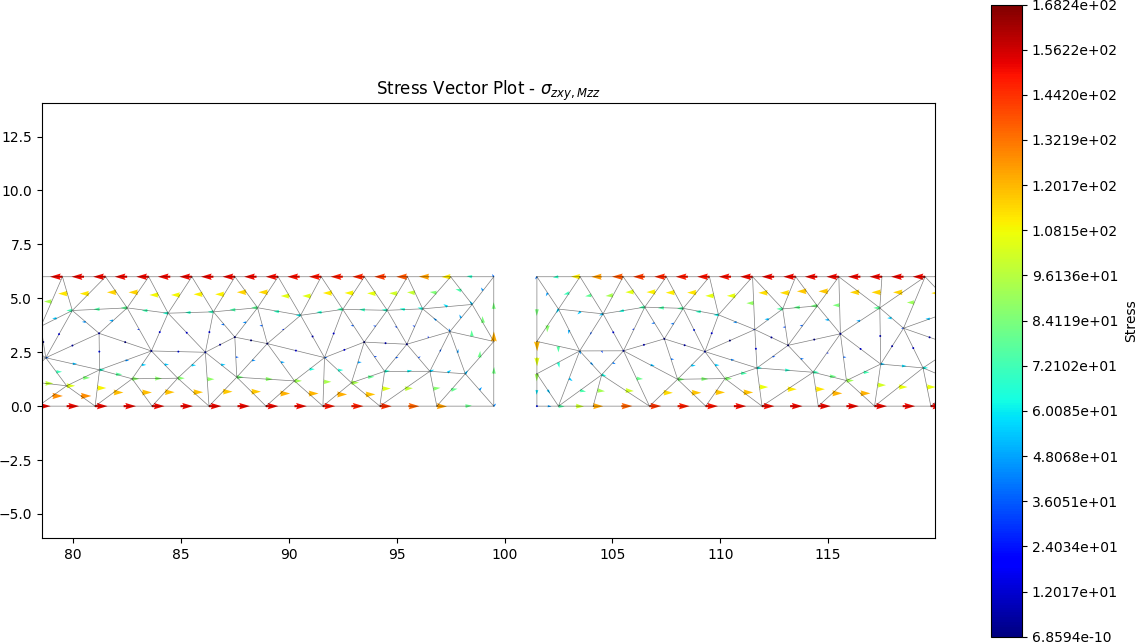
Split 200 x 100 x 6 RHS
A box section provides torsional stiffness by providing a closed path for shear stresses to flow at a considerable distance from a rotational centre. Preventing this enclosed path dramatically reduces the torsional rigidity of the section. This is illustrated through the analysis and of a 200 x 100 x 6 RHS, and a comparison to that of the same section with a 1 mm wide cut in one of the sides. A torsion of 1 kN.m is applied to both sections.
The analysis can be carried out with the following python commands:
import sectionproperties.pre.sections as sections
from sectionproperties.analysis.cross_section import CrossSection
# create RHS geometry
rhs_geometry = sections.Rhs(d=100, b=200, t=6, r_out=15, n_r=16)
# create split RHS geometry
split_geometry = sections.Rhs(d=100, b=200, t=6, r_out=15, n_r=16)
# create points at split
p1 = split_geometry.add_point([99.5, 0])
p2 = split_geometry.add_point([99.5, 6])
p3 = split_geometry.add_point([101.5, 0])
p4 = split_geometry.add_point([101.5, 6])
# create facets at split
split_geometry.add_facet([p1, p2])
split_geometry.add_facet([p3, p4])
split_geometry.add_hole([100, 3]) # add hole
split_geometry.clean_geometry() # clean the geometry
# create mesh and CrossSection objects
rhs_mesh = rhs_geometry.create_mesh(mesh_sizes=[2.5])
split_mesh = split_geometry.create_mesh(mesh_sizes=[2.5])
rhs_section = CrossSection(rhs_geometry, rhs_mesh)
split_section = CrossSection(split_geometry, split_mesh)
# plot the meshes
rhs_section.plot_mesh(pause=False)
split_section.plot_mesh()
# perform a geometric, warping analysis and stress analyses
print("CLOSED RHS:")
rhs_section.calculate_geometric_properties(time_info=True)
rhs_section.calculate_warping_properties(time_info=True)
rhs_stress = rhs_section.calculate_stress(Mzz=1e6, time_info=True)
print("\nSPLIT RHS:")
split_section.calculate_geometric_properties(time_info=True)
split_section.calculate_warping_properties(time_info=True)
split_stress = split_section.calculate_stress(Mzz=1e6, time_info=True)
# print torsional constants
print("Torsion Constants:")
print("CLOSED RHS: {0:.5e}".format(rhs_section.get_j()))
print("SPLIT RHS: {0:.5e}".format(split_section.get_j()))
# plot the stress
rhs_stress.plot_stress_mzz_zxy(pause=False)
rhs_stress.plot_vector_mzz_zxy(pause=False)
split_stress.plot_stress_mzz_zxy(pause=False)
split_stress.plot_vector_mzz_zxy()
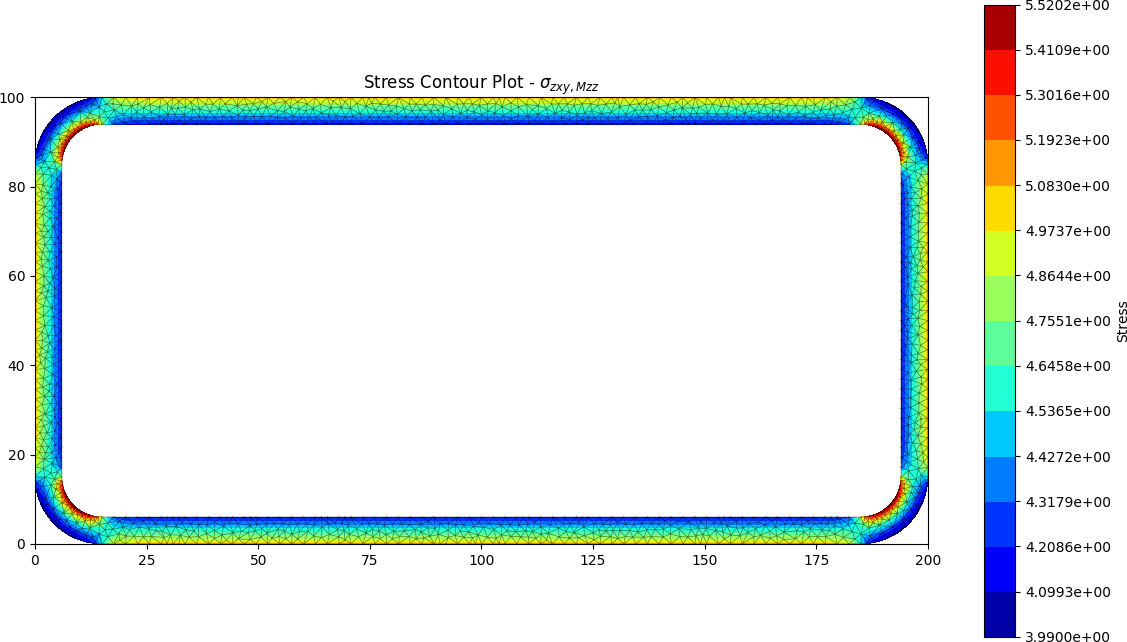
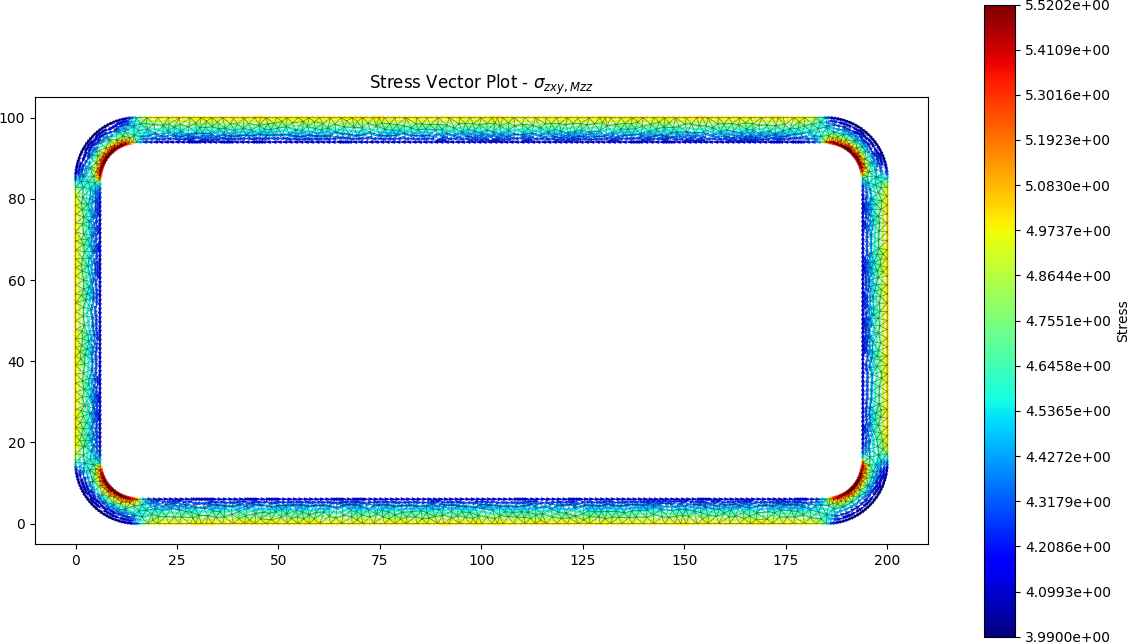
Closed RHS results
The torsion constant was calculated by the python package to be J = 14.236 x 106 mm4.

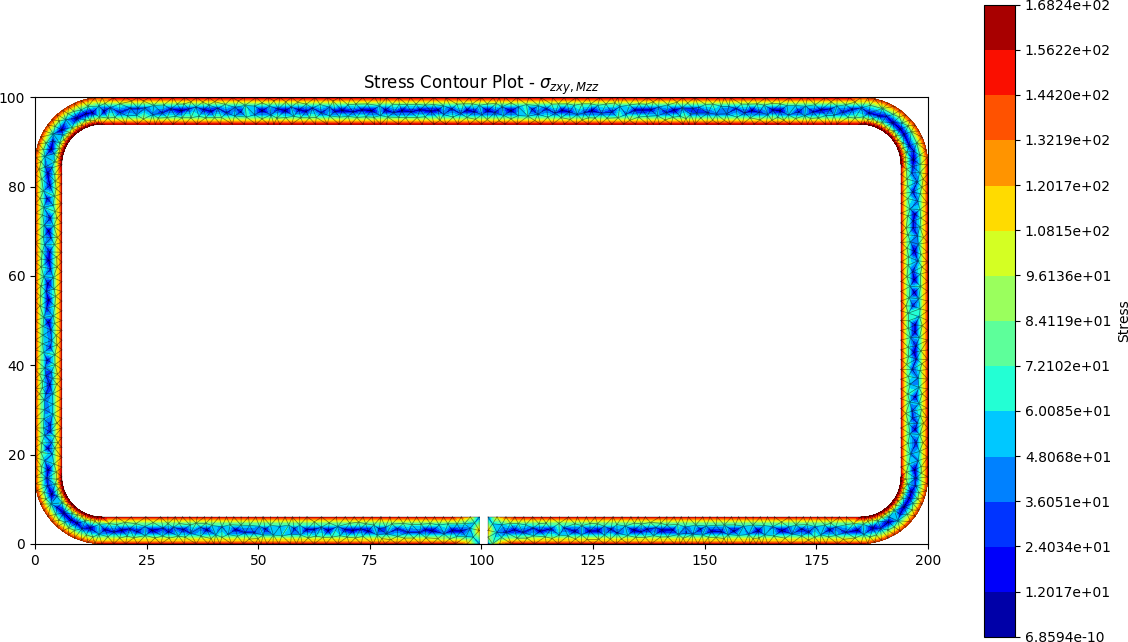
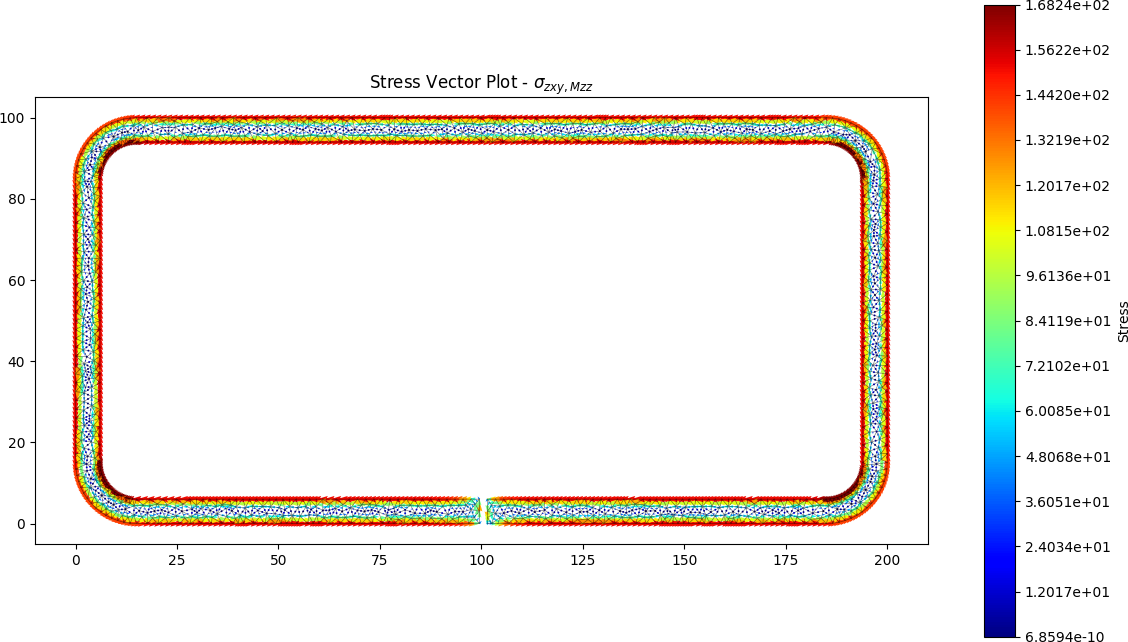
Split RHS results
The torsion constant was calculated by the python program to be J = 39.648 x 103 mm4, approximately 360 times less stiff than the closed section.

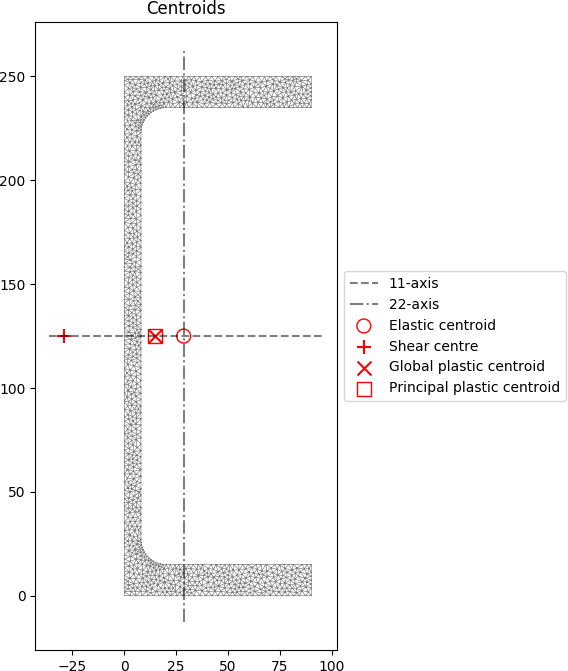
250 PFC
The analysis of a 250 PFC (250 mm deep parallel flange channel) can be carried out with the following python commands:
import sectionproperties.pre.sections as sections
from sectionproperties.analysis.cross_section import CrossSection
# create PFC geometry
geometry = sections.PfcSection(d=250, b=90, t_f=15, t_w=8, r=12, n_r=16)
# create a mesh
mesh = geometry.create_mesh(mesh_sizes=[4])
# create a CrossSection object
section = CrossSection(geometry, mesh)
# perform a geometric, warping and plastic analysis
section.calculate_geometric_properties()
section.calculate_warping_properties()
section.calculate_plastic_properties()
# plot the centroids
section.plot_centroids()
# get the torsion constant, warping constant and shear centre
print("Torsion Constant: {0:.5e}".format(section.get_j()))
print("Warping Constant: {0:.5e}".format(section.get_gamma()))
(cx, _) = section.get_c()
(x_s, _) = section.get_sc()
print("Shear Centre: {0:.5e}".format(x_s - cx))
This produces the following output for the warping dependent properties:
These results, which use a mesh size of 4 mm2, can be compared to the tabulated values in the OneSteel catalogue, and simple hand calculations. The OneSteel catalogue gives the following properties:
A mesh refinement study using the python cross-section package shows that the OneSteel value for the torsion constant is slightly (4%) overestimated, whereas the warping constant and shear centre show closer convergence. The numerical results obtained from the python package can be compared to simple hand calculations:
- Torsion Constant [1]
- Warping Constant [1]
- Shear Centre [2] (from centre of web to shear centre):
The above hand calculations align well with the results from the python package and the OneSteel catalogue.
Built-up 200UB25 + 150 x 100 x 9 RHS
A steel section is fabricated by placing a 150 x 100 x 9 RHS on its side on top of a 200UB25. The section is subjected to a major axis bending moment of 50 kN.m, a torsion moment of 10 kN.m and a y-direction shear force of -25 kN.
The analysis can be carried out by using the section builder function with the following python commands:
import sectionproperties.pre.sections as sections
from sectionproperties.analysis.cross_section import CrossSection
# create geometry
ub_geometry = sections.ISection(d=203, b=133, t_f=7.8, t_w=5.8, r=8.9, n_r=8, shift=[-66.5, 0])
rhs_geometry = sections.Rhs(d=100, b=150, t=9, r_out=22.5, n_r=8, shift=[-75, 203])
geometry = sections.MergedSection([ub_geometry, rhs_geometry]) # merge the sections
geometry.clean_geometry() # clean the geometry
# create a mesh
mesh = geometry.create_mesh(mesh_sizes=[5, 5])
# create a CrossSection object
section = CrossSection(geometry, mesh)
section.plot_mesh()
# perform a geometric, warping, plastic and stress analysis
section.calculate_geometric_properties()
section.calculate_warping_properties()
section.calculate_plastic_properties()
stress = section.calculate_stress(Mxx=50e6, Mzz=10e6, Vy=-25e3)
# plot the centroids
section.plot_centroids()
# plot the stress
stress.plot_stress_m_zz(pause=False)
stress.plot_stress_mzz_zxy(pause=False)
stress.plot_stress_v_zxy(pause=False)
stress.plot_stress_vm()
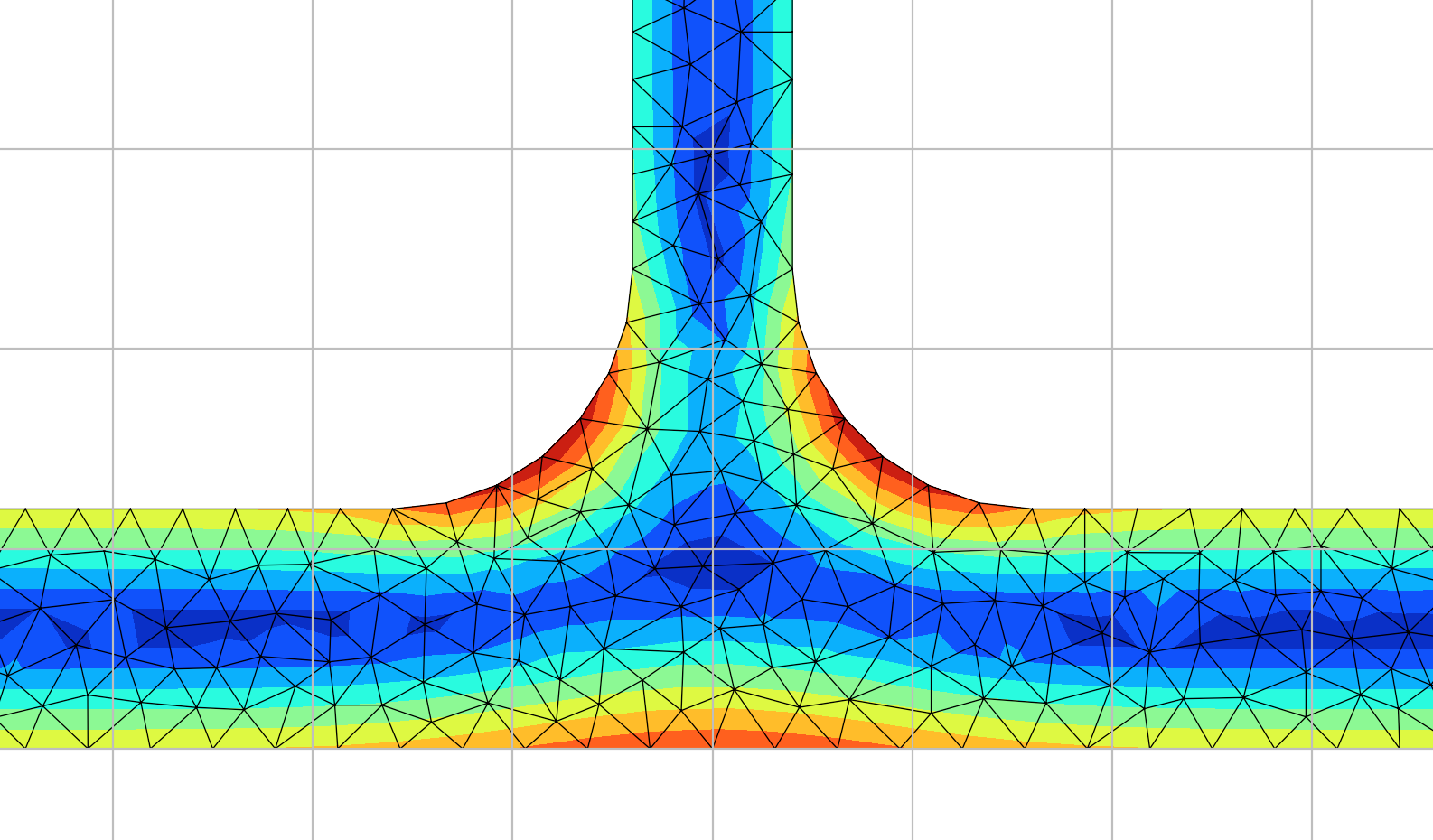
The centroids and stress contours are shown below:
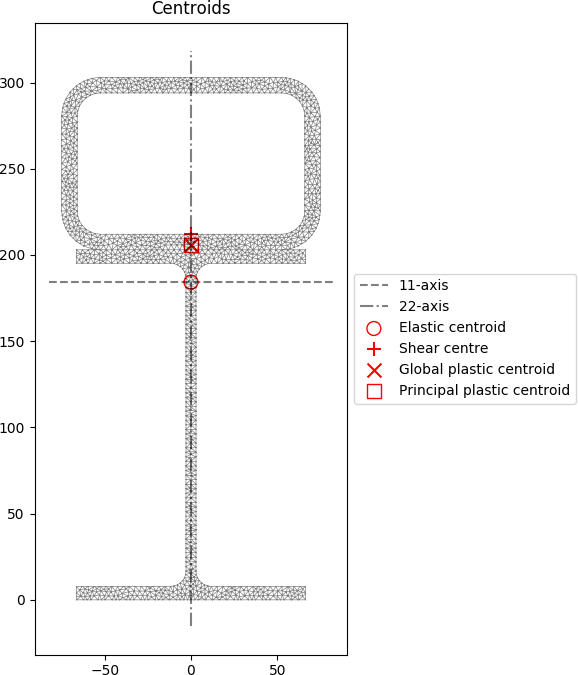
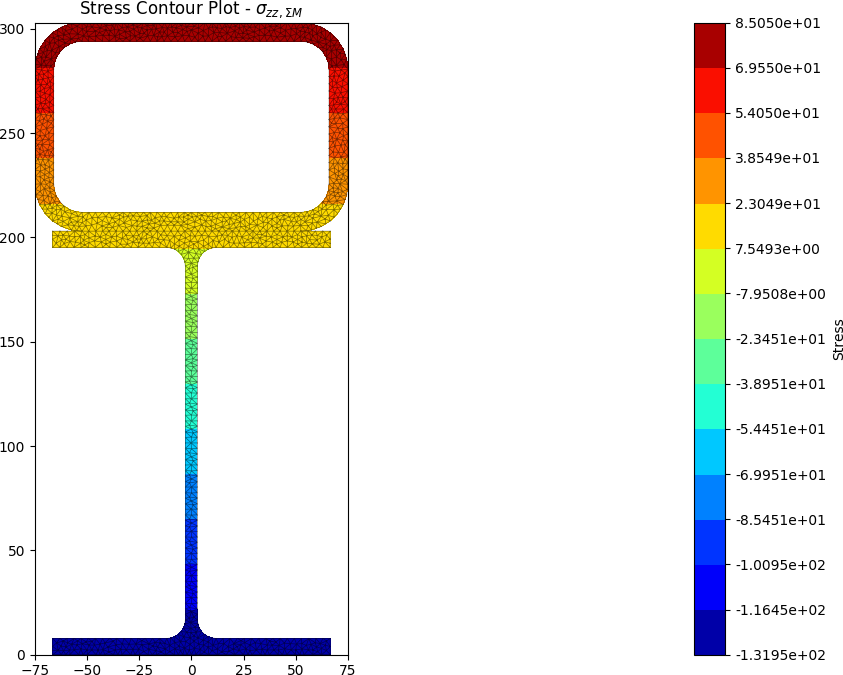
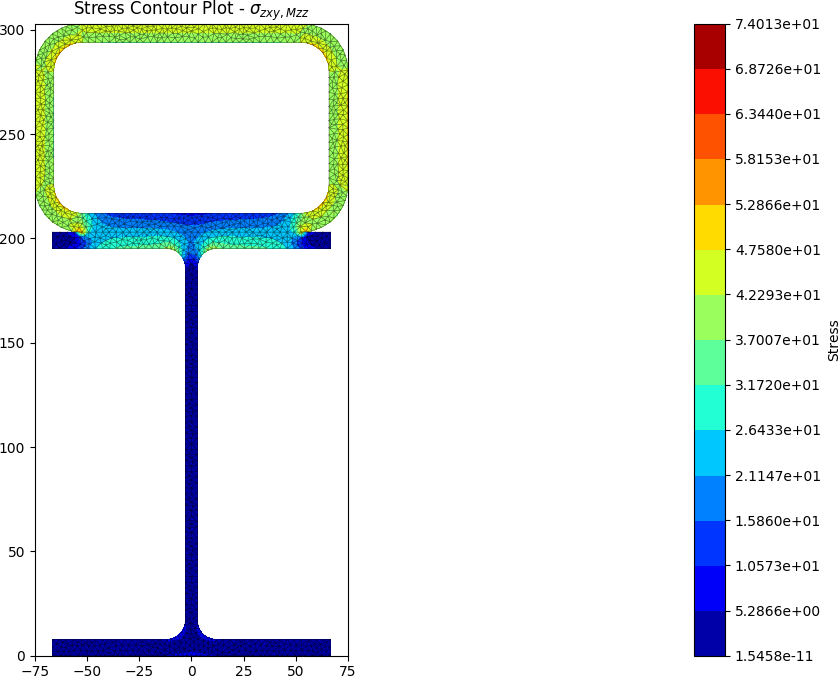
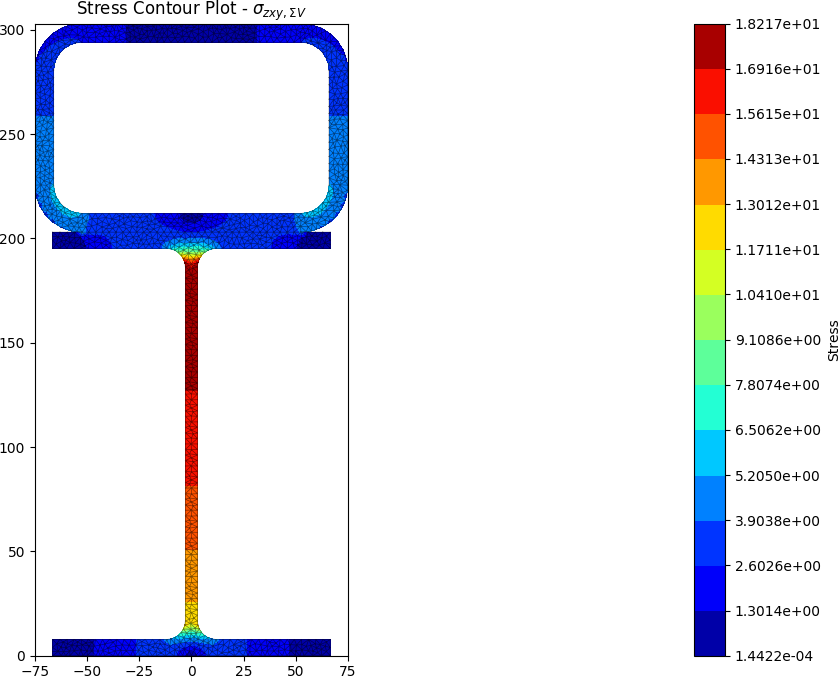
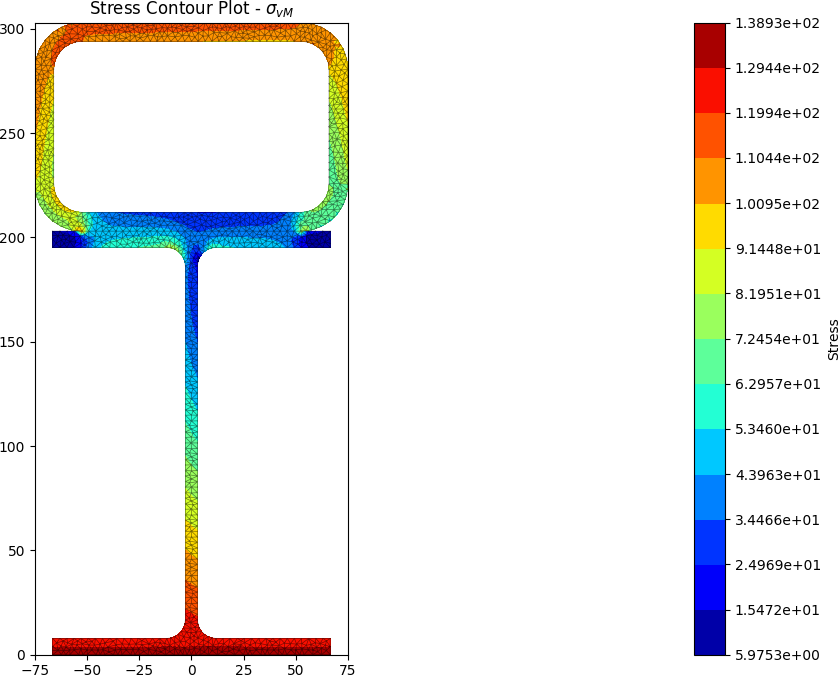
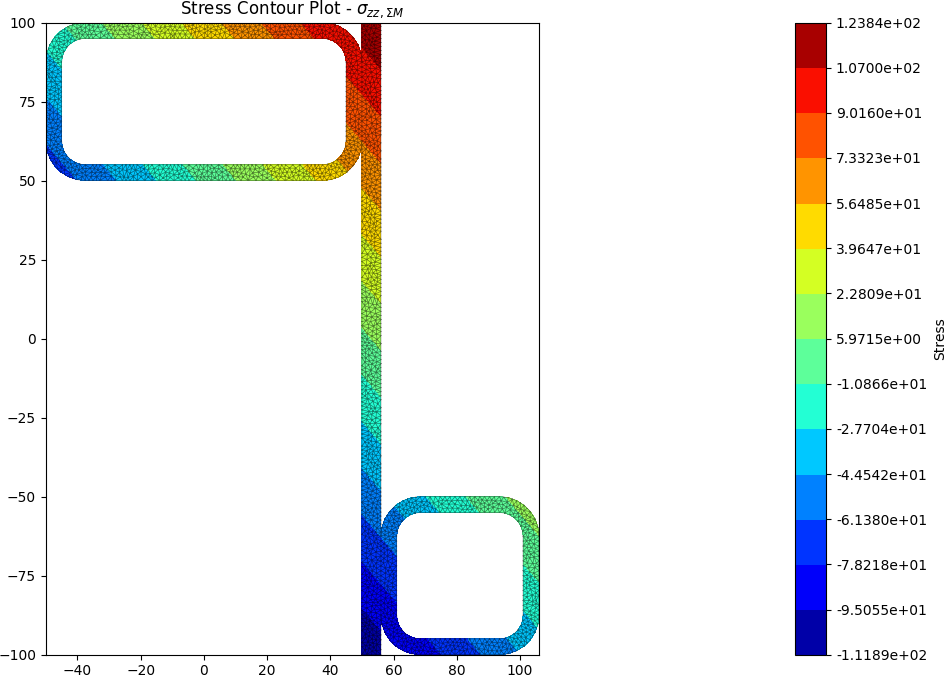
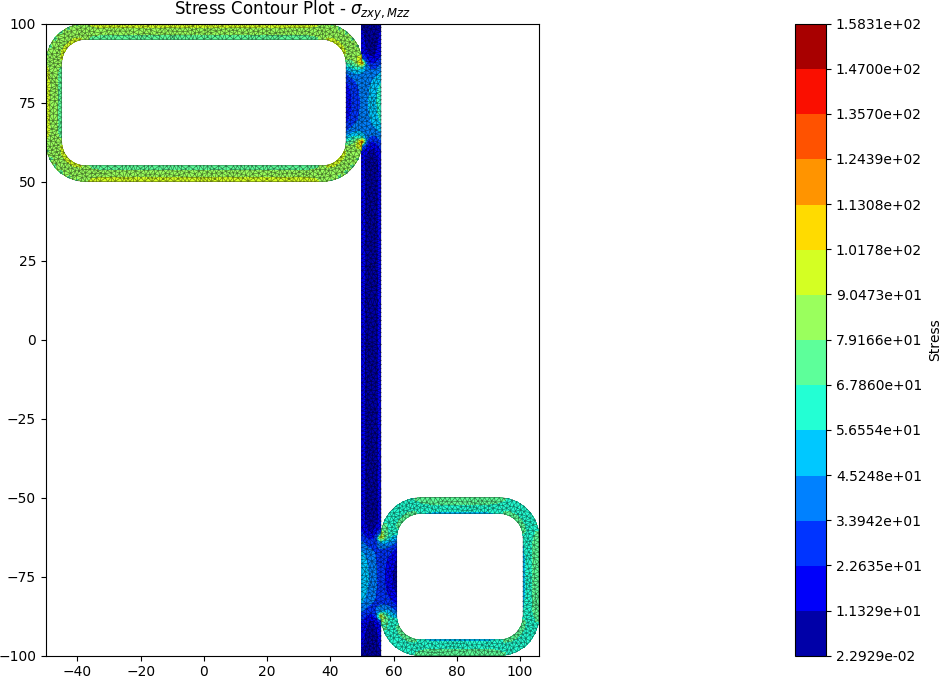
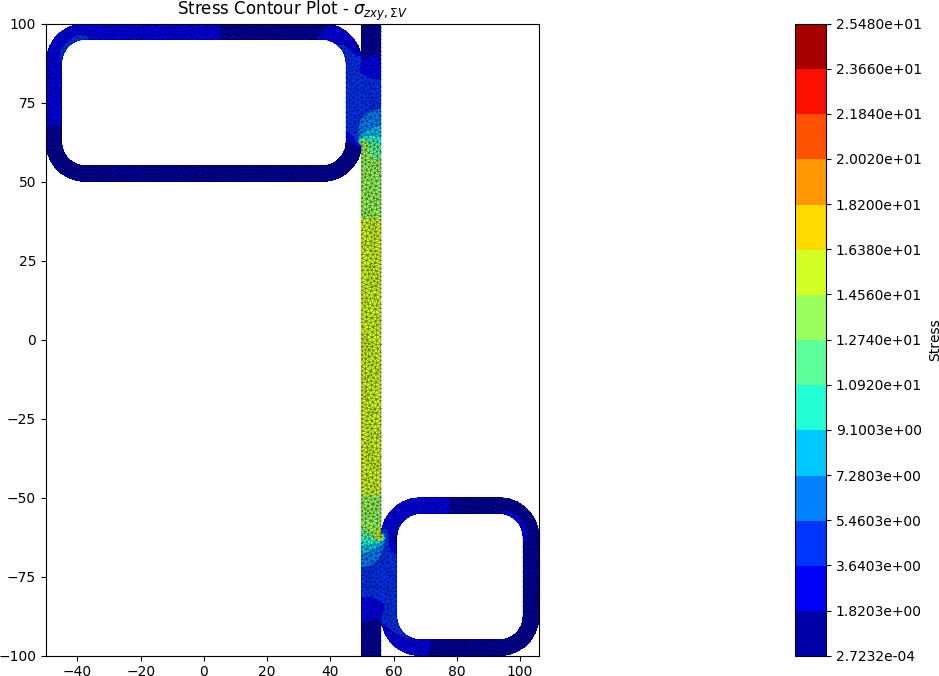
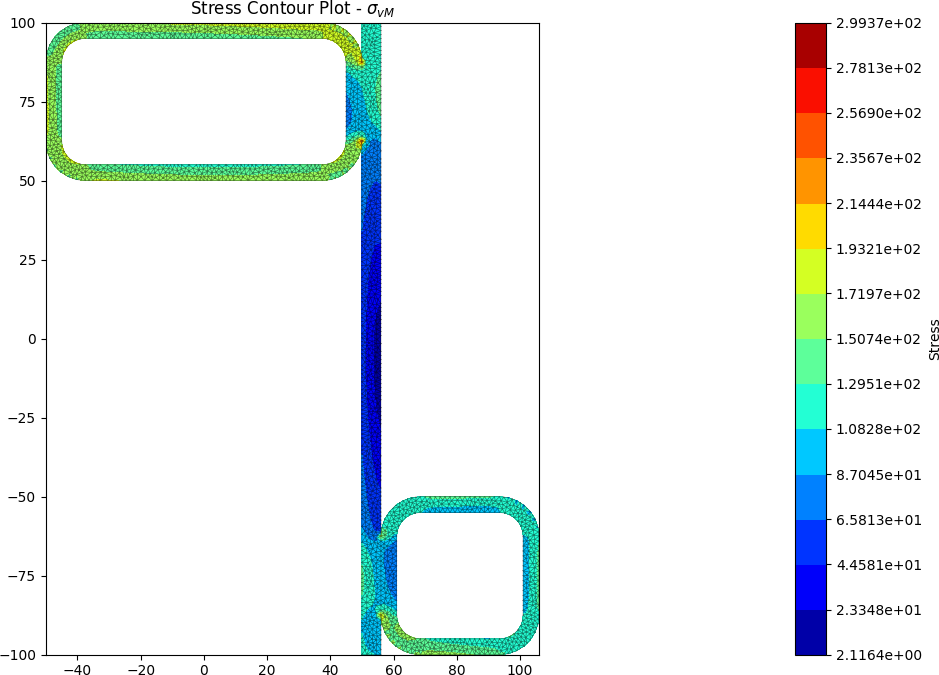
Built-up 50 x 5 SHS + 100 x 50 x 5 RHS + 200 x 6 Flat
A zed shaped steel section is fabriacted by welding a 50 x 5 SHS and a 100 x 50 x 5 RHS to a 200 x 6 flat section. The section is subjected to a major axis bending moment of 10 kN.m, a torsion moment of 5 kN.m and a y-direction shear force of -15 kN.
The analysis can be carried out by using the section builder function with the following python commands:
import sectionproperties.pre.sections as sections
from sectionproperties.analysis.cross_section import CrossSection
# create geometry
flat_geometry = sections.RectangularSection(d=200, b=6, shift=[50, -100])
shs_geometry = sections.Rhs(d=50, b=50, t=5, r_out=12.5, n_r=8, shift=[56, -100])
rhs_geometry = sections.Rhs(d=50, b=100, t=5, r_out=12.5, n_r=8, shift=[-50, 50])
# merge the sections
geometry = sections.MergedSection([flat_geometry, shs_geometry, rhs_geometry])
geometry.clean_geometry() # clean the geometry
# create a mesh
mesh = geometry.create_mesh(mesh_sizes=[1.5, 1.5, 1.5])
# create a CrossSection object
section = CrossSection(geometry, mesh)
section.plot_mesh()
# perform a geometric, warping, plastic and stress analysis
section.calculate_geometric_properties()
section.calculate_warping_properties()
section.calculate_plastic_properties()
stress = section.calculate_stress(Mxx=10e6, Mzz=5e6, Vy=-15e3)
# plot the centroids
section.plot_centroids()
# plot the stress
stress.plot_stress_m_zz(pause=False)
stress.plot_stress_mzz_zxy(pause=False)
stress.plot_stress_v_zxy(pause=False)
stress.plot_stress_vm()
The centroids and stress contours are shown below:
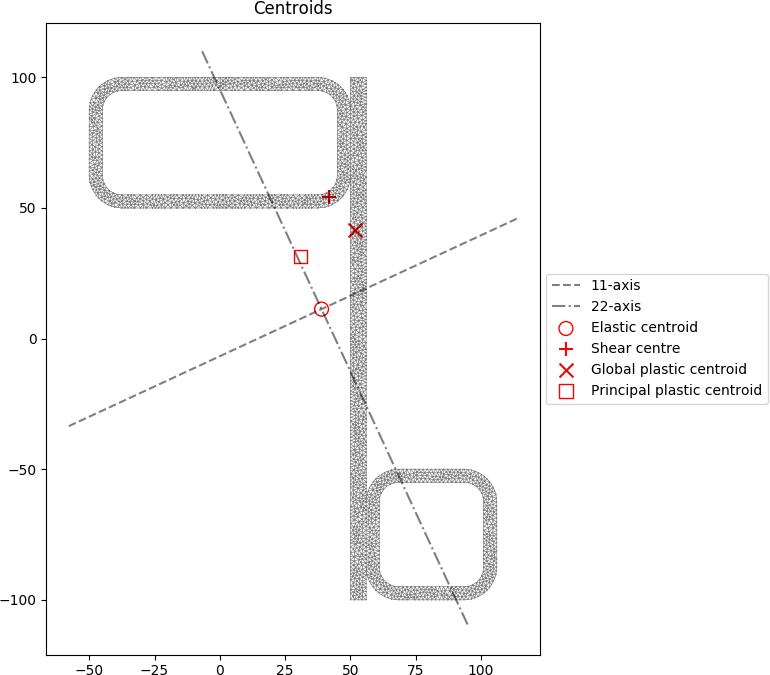
References
- AS 4100-1998: Steel Structures
- W.D. Pilkey, Analysis and Design of Elastic Beams: Computational Methods, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 2002.




Leave a comment